- +94 77 860 6688
- [email protected]
Bringing international gem testing standards to the Sri Lankan gem industry
Reports & Verification
expert evaluation, and transparency in the trade
Verify Now
Report Before Oct 2024 Verify Now
Report After Oct 2024
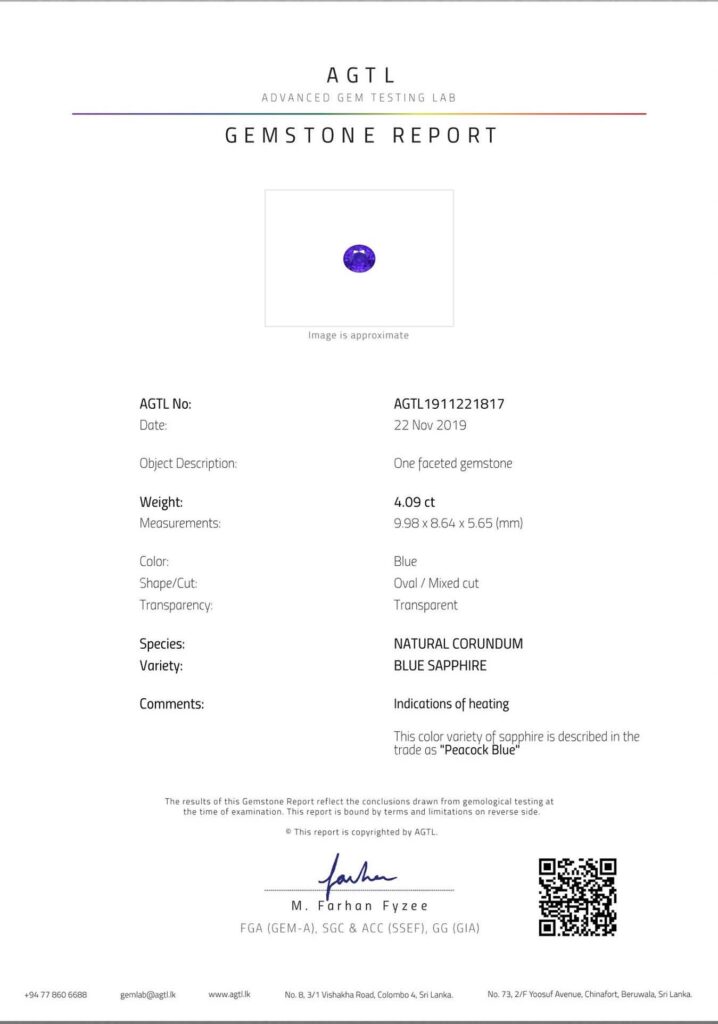
STRUCTURE ALL REPORTS
AGTL Report Structure
Image
Image depicts the gem at the time of testing. The image on the AGTL report serves a symbolic purpose and may not accurately depict the actual attributes such as colour, clarity, or size.
AGTL Number
AGTL number is a distinctive identifier assigned to an object when it is submitted for evaluation, ensuring its uniqueness and can be used to verify the report.
Date
The date in which the object was brought in for testing
Object Description
Description of the object brought in for testing
Weight
Gem weight refers to the mass of a gemstone, typically measured in carats. The carat is a standardised unit of weight used for gemstones, with one carat equal to 200 milligrams.
Gem weight is a crucial factor in assessing a gem’s value and is often associated with its size, although it’s important to note that two gemstones of the same weight may appear differently in size based on their specific density and proportions.
The weight of a gem is one of the four Cs (carat, cut, colour, and clarity) that are used to evaluate and classify gemstones, especially in the context of diamond grading.
Carat weight can significantly influence a gem’s price, with larger gemstones often being more valuable due to their relative rarity.
Measurements
Gem measurements refer to the physical dimensions of a gemstone, typically specified in millimeters. These measurements include the gem’s length, width, and depth or thickness, and they are used to describe the size and proportions of the gem.
Precise measurements are crucial in assessing a gem’s value and quality, as they impact its appearance, weight, and suitability for specific jewelry settings. The measurements are often taken across the widest parts of the gem’s surface and may be used to calculate its weight (carat) and proportions, which affect how light interacts with the stone, influencing its brilliance and overall visual appeal.
Accurate gem measurements are essential for gemological grading and for selecting stones that fit specific jewelry designs.
Color
Gem colour refers to the perceived hue or shade of a gemstone, which is one of its most defining and valuable characteristics. The color of a gem is determined by the specific wavelengths of light it absorbs and reflects, and it can range from a variety of hues and tones. For example, diamonds are often valued for their lack of colour, appearing transparent or white, while sapphires come in various colour like blue, pink, or yellow.
The colour of a gemstone can be influenced by various factors, including the presence of trace elements and impurities in its crystal structure, and it plays a significant role in its desirability and value. Gem colour is often assessed on scales that consider hue, tone (lightness or darkness), and saturation (vividness or intensity).
Shape / Cut
Gem shape, also known as the cut, refers to the way a gemstone has been fashioned or faceted from its raw or rough form into a specific geometric design. The cut or shape of a gem significantly influences its overall appearance, brilliance, and how it interacts with light.
Common gem cuts include round, oval, pear, emerald, and princess cuts, among others. Different cuts are chosen to highlight a gem’s unique features, such as colour, clarity, and the way it sparkles when exposed to light. The cut is a crucial factor in the grading and valuation of gemstones.
Transparency
Gem transparency refers to how easily light can pass through a gemstone. It describes the degree to which the gem allows light to travel through it, affecting its visual appearance. Gemstones can vary from transparent (where light passes through clearly) to translucent (allowing some light with diffusion) to opaque (blocking light entirely). Transparency is an important factor in assessing a gem’s quality and value.
Species
Gem species in the context of gemstones are mineral groups with similar properties, sharing chemical composition and structure. Examples include beryl (emerald, aquamarine) and garnet (pyrope, almandine), each having distinct varieties with unique colours. This classification aids in identifying and appreciating the diversity of gemstones.
Variety
A gem variety refers to different forms or types of a particular gem mineral, characterised by variations in colour, appearance, or other distinctive features. For example, sapphire is a gem variety of the mineral corundum, and it can come in various colours like blue, pink, or yellow. These variations within the same mineral species are referred to as different gem varieties.
Comments
Comments including indications of heating and more information
Signature
Signed by our Gemologist
QR Code
A unique QR code to verify that report’s authenticity. Using a smart device with a QR-scanner app, scan the code and verify if the report appears in our database. Alternatively, you can go to our Report Verification page.
Our Contact
Contact us through call, Whatsapp and email:
-
No. 73, 2/F,Yoosuf Avenue, Chinafort,
Beruwala, Sri Lanka - +94 77 860 6688
- [email protected]
General
Important
Gallery






© 2025 THE WEB SUSHI | All Rights Reserved
